This is most prevalent within the field of gas turbine manufacturing Gas turbine blades are some of the most critical components within a gas turbine engine. These improve the working of the engine and make it function smoothly. In this article, we will discuss how gas turbine blades are designed, their manufacturing materials, and their airflow. We will also discuss new concepts, and enhancements in this field.
Gas Turbine Engine integrated with airflow SATCOM. Gas Turbine Blades Location The turbine. These blades extract energy from hot gas produced in the combustion chamber and convert it into rotational energy. This whirling energy assists the compressor and generates power.
Gas turbine blade design plays a very important role in gas turbine performance. The blades' shape and size must be meticulously designed to ensure they are effective and durable. Many gas turbines employ blades shaped like an aerofoil because the shape delivers better airflow and less drag. The blades also face high temperatures and great forces, thus must be made with materials that can withstand such adverse conditions.
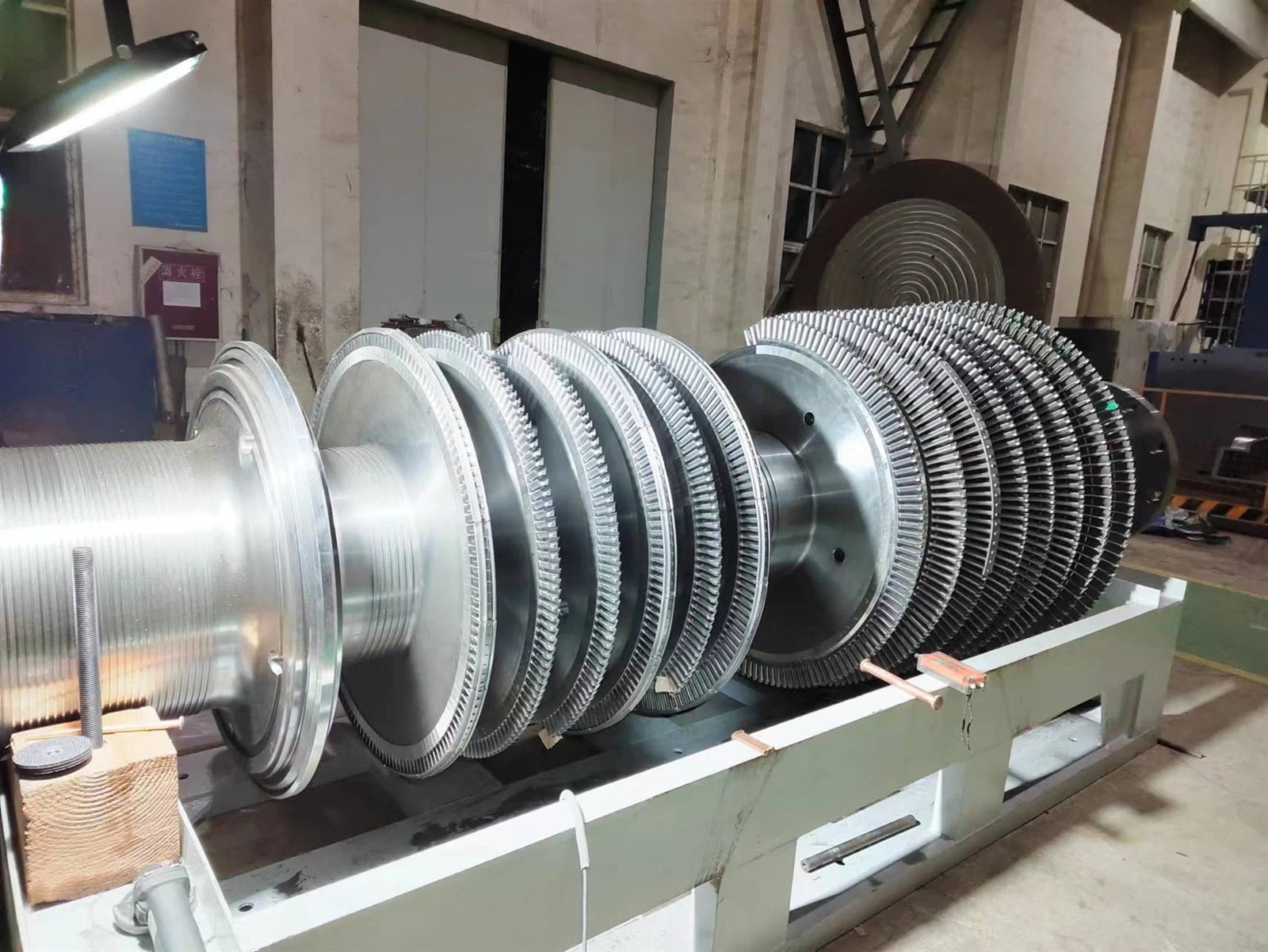

It is crucial to choose the right materials for combined cycle gas turbine power plants. The blades are typically constructed of high-strength, heat resistant materials such as nickel-based superalloys or ceramic composites. Such materials are incredibly robust, making them capable of withstanding temperatures beyond 1000°C; therefore, the selection of appropriate materials is critical to ensure that gas turbine blades are both reliable and long-lasting.

Gas turbine blades also rely heavily on aerodynamics, or how air flows around them. The objective in the shape of blades is to make the air flow easy with minimum losses. Meanwhile, smooth surfaces minimize drag and optimize the engine performance. The angle and twist of the blades also have to be just right in order to extract as much energy as possible from the flow of gas.
Breakthroughs in the design of gas turbine blades have brought about enhancements in engine performance. For example, 3D printing allows complex blade designs with unique cooling channels inside to be manufactured. This allows the blades to operate cooler and preserves their life span. New coatings and surface treatments also protect against damage, which allows the blades to last even longer.”
Dongturbo Electric Company Ltd (DTEC). is an international corporation, with its headquarter in Chengdu, China, and manufacturing bases in Deyang and Kunming, China, mainly engaged in the manufacturing of power electric equipments, EPCC(engineering, procurement, construction, commissioning), investment & finance, and export and import business. DTEC also has branches and joint venture in Malaysia, Thailand and the Philippines. Our business scope covers EPC, supply equipments and materials for thermal power including boiler, turbine, generator and their auxiliaries, BOP, electric and C& I etc; EPC and equipment supply for PV, thermal solar power, Wind &PV hybrid and energy storage system; spare parts supply and power plant.
Committed to excellence in every aspect of our business, we prioritize building long-lasting relationships with our customers that extend beyond mere transactions. We understand that our clients’ success is our success, and this drives us to consistently deliver not only high-quality products but also exceptional service. Our team is always prepared to go the extra mile, proactively addressing any challenges and anticipating the needs of our customers. By fostering open communication and actively seeking feedback, we ensure that we remain aligned with their goals and expectations. This customer-centric approach allows us to tailor our solutions and support, ultimately enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction. We believe that through these strong partnerships, we can create mutual growth and success, paving the way for a prosperous future together.
Our unwavering commitment to research and development is a cornerstone of our operations, enabling us to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving landscape of power generation technology. By continually investing in innovative practices and the latest advancements, we ensure that our products not only meet but exceed industry standards. This dedication allows us to provide our clients with cutting-edge solutions that are tailored to their unique operational needs. Each customized product is designed to deliver maximum value and efficiency, ultimately empowering our clients to optimize their processes, reduce costs, and enhance their overall productivity. Through this proactive approach, we not only bolster our position as a leader in the industry but also contribute to the sustainable growth of our partners in power generation.
We are a leading global manufacturer and supplier of power generation equipment, dedicated to serving clients worldwide. Our commitment to excellence goes beyond merely providing products; we understand that our success is intrinsically linked to the prosperity of our customers. By prioritizing their needs and challenges, we aim to develop innovative solutions that enhance their operations and drive their growth. Our extensive experience in the industry enables us to offer tailored support, ensuring that each client receives the highest level of service and quality. As we continue to expand our reach, we remain focused on fostering strong partnerships that empower our clients and contribute to a sustainable future in power generation.